A) later had difficulty distinguishing color and brightness.
B) later had difficulty perceiving color and brightness, but eventually regained normal sensitivity.
C) later had difficulty perceiving the shape of objects.
D) showed no impairment in perception, indicating that neural feature detectors develop even in the absence of normal sensory experiences.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are laws of perceptual organization EXCEPT
A) proximity.
B) closure.
C) continuity.
D) retinal disparity.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People who demonstrate blindsight have most likely suffered damage to their
A) cornea.
B) lens.
C) fovea.
D) visual cortex.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Immanuel Kant and John Locke would have been most likely to disagree about the extent to which perception is influenced by
A) cultural experience.
B) retinal disparity.
C) accommodation.
D) relative luminance.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jody's horse looks just as black in the brilliant sunlight as it does in the dim light of the stable. This illustrates what is known as
A) synaesthesia.
B) sensory interaction.
C) brightness constancy.
D) the phi phenomenon.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The receptor of the eye that functions best in dim light is the
A) fovea.
B) cone.
C) bipolar cell.
D) rod.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ewald Hering found a clue to the mystery of color vision in
A) blindsight.
B) afterimages.
C) retinal disparity.
D) the phi phenomenon.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is consistent with the Gestalt theory of perception?
A) Perception develops largely through learning.
B) Perception is the product of heredity.
C) The mind organizes sensations into meaningful perceptions.
D) Perception results directly from sensation.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multiple ________ send combined messages to a bipolar cell, whereas a single ________ may link directly to a single bipolar cell.
A) rods; cone
B) cones; rod
C) hair cells; basilar membrane
D) basilar membranes; hair cell
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jack claims that he often has dreams that predict future events. He claims to have the power of
A) telepathy.
B) clairvoyance.
C) precognition.
D) psychokinesis.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The feature detectors identified by Hubel and Weisel consist of
A) nerve cells in the brain.
B) rods and cones.
C) bipolar cells.
D) ganglion cells.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Retinal disparity refers to the
A) tendency to see parallel lines as coming together in the distance.
B) tendency to see stimuli that are near each other as parts of a unified object.
C) somewhat different images our two eyes receive of the same object.
D) inability to distinguish figure from ground.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure-ground relationship has demonstrated that
A) perception is largely innate.
B) perception is simply a point-for-point representation of sensation.
C) the same stimulus can trigger more than one perception.
D) different people see different things when viewing a scene.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The way in which you quickly group the individual letters in this test item into separate words best illustrates the principle of
A) closure.
B) proximity.
C) interposition.
D) perceptual constancy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The perception of the letter "t" as two intersecting lines rather than as four nonintersecting lines illustrates the principle of
A) accommodation.
B) proximity.
C) closure.
D) continuity.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You probably perceive the diagram below as three separate objects due to the principle of 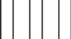
A) proximity.
B) continuity.
C) closure.
D) retinal disparity.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Objects are brought into focus on the retina by changes in the curve and thickness of the
A) rods and cones.
B) lens.
C) bipolar cells.
D) optic nerve.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure is to ground as ________ is to ________.
A) night; day
B) top; bottom
C) cloud; sky
D) sensation; perception
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The historical movement associated with the statement "The whole may exceed the sum of its parts" is
A) parapsychology.
B) behavioral psychology.
C) functional psychology.
D) Gestalt psychology.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Knowing about the effects of the perceived distance of objects on their perceived size helps us to understand
A) the Moon illusion.
B) the McGurk effect.
C) prosopagnosia.
D) light and shadow.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 165
Related Exams