A) Trisomy-21
B) Leukemia
C) Cystic fibrosis
D) Huntingtons
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher wants to create a mouse model for a disease, to allow her team to study possible therapies.The disease is known to be caused by a small deletion that removes a certain gene.Which type of mouse would be the best choice for this purpose?
A) Knockout mouse
B) Knockin mouse
C) Conditional knockout mouse activated by a drug
D) Mutant derived by traditional forward genetics screen
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A medical researcher is trying to develop a diagnostic technique for a disease which is characterized by replication of a particular chromosomal region.What would be the most appropriate technique?
A) FISH
B) Gene chip
C) Genome sequencing
D) White blood cell count
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enzymes that cleave DNA at specific sites are called _____________.
A) vectors
B) peptidases
C) restriction endonucleases
D) DNAses
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some ciliate protozoa, the codons UAA and UAG encode glutamate, rather than acting as STOP codons.How does this compare to other species?
A) This is unusual - almost all species share the same "universal" genetic code.
B) This is typical - every species has its own unique genetic code.
C) This is not unusual - while most species have a similar genetic code, there are often variations for some of the amino acids.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Restriction enzymes are
A) proteases.
B) lipases.
C) endonucleases.
D) exonucleases.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A friend makes the argument that transgenic crops have only been used to enrich large corporations, not to improve people's health.What is the best counterexample?
A) Golden rice
B) Bt maize
C) Glyphosate-resistant soybeans
D) Cre-Lox
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify a sequence that is most likely to be recognized by a restriction enzyme.
A) CGATGC
B) CCCTTT
C) TGGCCA
D) TCATCA
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Single-stranded complementary tails that are produced by restriction digestion are called ______ ends.
A) sticky
B) orphaned
C) vectors
D) 5'
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Single-stranded ends generated by the same restriction enzyme are complementary to each other.They can be joined together,
A) even when the source of the DNA is different.
B) only when the source of the DNA is the same.
C) but the "sticky ends" will most likely have to be modified.
D) but the hybridization of the two ends may cause a problem with cloning.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 6.85 kb EcoRI fragment of DNA is shown below.The location of several restriction sites is indicated.Scale is approximate. 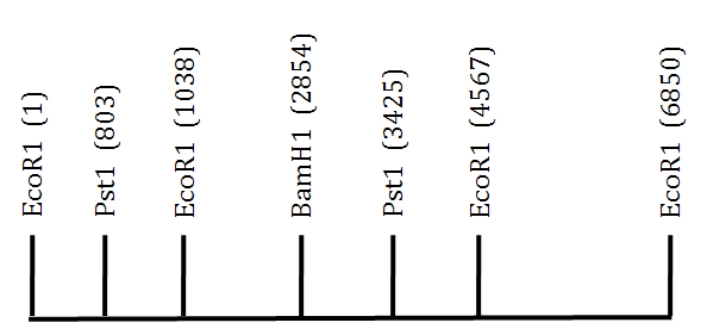 If you were to digest this DNA with PstI, which length of DNA fragment would migrate the fastest on an agarose gel?
If you were to digest this DNA with PstI, which length of DNA fragment would migrate the fastest on an agarose gel?
A) 803
B) 2622
C) 3425
D) 235
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A commercially significant human protein now produced in bacteria is
A) hemoglobin.
B) gamma globulins.
C) AZT.
D) human insulin.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small circular, extrachromosomal DNA segments are known as _______.
A) vectors
B) plasmids
C) clones
D) RNA
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An insecticidal protein has been discovered in a bacterium known as
A) Escherichia coli.
B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
C) Bacillus thuringiensis.
D) Aspergillus sp.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are the scientific consultant for a television show about forensic analysis.In an upcoming episode, investigators will compare the DNA of a suspect and a DNA sample collected from the victim's fingernails.You are to write up a brief explanation of the technique required for comparing the DNA.Which technique should you explain?
A) DNA fingerprinting
B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization
C) RNAi
D) RT-PCR
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of information would be most useful in an effort to move a DNA fragment from one plasmid vector to another, using molecular cloning techniques?
A) DNA fingerprint data
B) sequence of PCR primers
C) data from cloning of Dolly the sheep
D) restriction maps of the plasmids
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 6.85 kb EcoRI fragment of DNA is shown below.The location of several restriction sites is indicated.Scale is approximate. 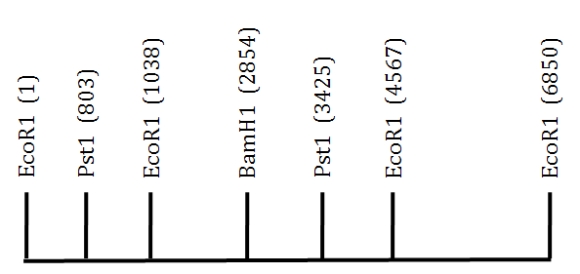 If you were to completely digest this fragment of DNA with PstI, how many pieces of DNA would you obtain?
If you were to completely digest this fragment of DNA with PstI, how many pieces of DNA would you obtain?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fourth type of restriction enzyme is identified that cleaves at precise locations like a type II enzyme, but it also occasionally makes mistakes and cuts elsewhere.Would this type of enzyme be a useful enzyme to use in molecular cloning?
A) Yes, because it cuts correctly sometimes.
B) No, because it is a precise enzyme.
C) No, because cutting mistakes could lead to incorrect cloning.
D) Yes, because cutting mistakes don't matter in molecular cloning.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three scientists are using different forms of PCR for their research.Abby wants to determine changes in gene expression levels in a tissue, so she uses ______.Bob is trying to extract genetic information from a wooly mammoth fossil, so he uses ______.Chris needs to express a gene in bacteria that matches the form expressed in kidney cells, so she uses ______.
A) Quantitative RT-PCR; PCR; RT-PCR
B) PCR; quantitative RT-PCR; RT-PCR
C) RT-PCR; PCR; quantitative RT-PCR
D) RT-PCR; quantitative RT-PCR; PCR
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 39 of 39
Related Exams