B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Patientʹs serum, influenza virus, and red blood cells are mixed in a tube. What happens if the patient has antibodies against influenza virus?
A) hemolysis
B) agglutination
C) hemagglutination
D) complement fixation
E) hemagglutination-inhibition
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an immunodiffusion test to diagnose the fungal disease histoplasmosis, a patientʹs serum is placed in a well in an agar plate. In a positive test, a precipitate forms as the serum diffuses from the well and meets material diffusing from a second well. In this test process, what is the most likely identity of the material in the second well?
A) red blood cells
B) a purified fungal antigen
C) a purified protozoan antigen
D) antibodies
E) entire fungal cells
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Western blotting uses antibodies to detect specific proteins in a mixture of proteins.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inactivated tetanus toxin is a(n)
A) nucleic acid vaccine.
B) conjugated vaccine.
C) subunit vaccine.
D) toxoid vaccine.
E) inactivated whole-agent vaccine.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a pregnancy test used to find the fetal hormone HCG in a womanʹs urine using anti-HCG and latex spheres?
A) neutralization reaction
B) immunofluorescence
C) precipitation reaction
D) direct agglutination reaction
E) indirect agglutination reaction
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following steps are used to produce monoclonal antibodies. What is the fourth step?
A) Culture the hybridoma in a selective medium.
B) A B cell is activated to produce antibodies.
C) Isolate antibody-producing B cells.
D) Vaccinate a mouse.
E) Fuse a B cell to a myeloma cell.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a test to determine the presence of soluble antigens in a patientʹs saliva?
A) immunofluorescence
B) precipitation reaction
C) passive agglutination reaction
D) neutralization reaction
E) direct agglutination reaction
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 18.1 Antibody Titer -In Table 18.1, who probably has the disease?
A) Patients A and C
B) Patients A and D
C) Patients B and C
D) Patients C and D
E) Patients A and B
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reaction between an antibody and soluble antigen-forming lattices is called a(n)
A) agglutination reaction.
B) complement fixation.
C) immunofluorescence.
D) neutralization reaction.
E) precipitation reaction.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Blood typing tests are examples of hemagglutination reactions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of live attenuated vaccine agents?
A) They occasionally revert to virulent forms.
B) They require few or no booster immunizations.
C) The immune response generated by the vaccine closely mimics a real infection.
D) They stimulate by cell-mediated and humoral immune responses.
E) They elicit lifelong immunity.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an agglutination test, eight serial dilutions to determine antibody titer were set up. Tube #1 contained a 1:2 dilution; tube #2, a 1:4, etc. If tube #6 is the last tube showing agglutination, what is the antibody titer?
A) 6
B) 1:6
C) 1:32
D) 32
E) 64
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 18.1
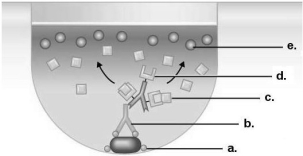 -Which component in Figure 18.1 came from the patient in this indirect ELISA test?
-Which component in Figure 18.1 came from the patient in this indirect ELISA test?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following uses fluorescent-labeled antibodies?
A) neutralization
B) complement fixation
C) precipitation
D) flow cytometry
E) agglutination
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which item is from the patient in a direct ELISA test?
A) antigen
B) antibodies against the antigen
C) antihuman immune serum
D) substrate for the enzyme
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of vaccine involves host synthesis of viral antigens?
A) nucleic acid vaccine
B) attenuated whole-agent vaccine
C) conjugated vaccine
D) toxoid vaccine
E) subunit vaccine
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Agglutination tests use particulate antigens while precipitation tests use soluble antigens.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ELISA for Hepatitis C has 95 percent sensitivity and 90 percent specificity. This means that the test
A) detects 95 percent of the true positive samples and has 90 percent false positive results.
B) detects 5 percent of the true positive samples and has 90 percent false positive results.
C) detects 95 percent of the true positive samples and has 10 percent false positive results.
D) detects 5 percent of the true positive samples and has 10 percent false positive results.
E) detects 90 percent of the true positive samples and has 5 percent false positive results.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Purified protein from Bordetella pertussis is used in a(n)
A) nucleic acid vaccine.
B) subunit vaccine.
C) toxoid vaccine.
D) attenuated whole-agent vaccine.
E) conjugated vaccine.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 55
Related Exams