A) lyases.
B) synthases.
C) synthetases.
D) oxidoreductases.
E) hydrolases.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Affinity labels are radioactive competitive inhibitors used to identify the most important residues in an enzymeʹs active site.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hydrophobic cleft in globular proteins which bind substrate molecules is called the .
A) substrate pocket
B) modulator site
C) active site
D) activity site
E) oligomeric site
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When varying the substrate concentration at a fixed concentration of enzyme it is observed that at low concentrations of substrate the reaction is ,while at high concentrations of substrate the reaction is .
A) maximal; initial
B) initial; maximal
C) second order; first order
D) first order; second order
E) first order; zero order
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Enzymes make reactions 103 to 1020 times faster.
B) Enzymes lower the amount of energy needed for a reaction.
C) Enzymes are chemically unchanged during the actual catalytic process.
D) Enzymes speed up the attainment of a reaction equilibrium.
E) Enzymes are proteins.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which equilibrium below applies to noncompetitive inhibition? 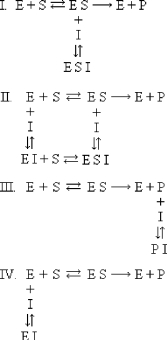
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concentrations of enzymes are determined by using pseudo first-order conditions in which
A) S concentration is kept the same and the rate is measured.
B) E concentration is kept the same and the rate is measured.
C) S concentration is constant, E concentration varied and the rate is measured.
D) E concentration is constant, S concentration varied and the rate is measured.
E) All of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unlike typical catalyzed reactions in organic chemistry enzyme reactions are
A) usually stereospecific.
B) reaction specific.
C) essentially 100% efficient.
D) modulated to change activity levels.
E) All of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not an explanation of why site-directed mutagenesis is a more powerful tool than many other techniques for determining important residues in an enzyme?
A) It is a more specific technique than irreversible inhibition experiments.
B) It can be used on enzymes for which no specific irreversible inhibitor is known.
C) It allows for testing of the specific function of amino acid side chains in an enzyme.
D) It is especially useful for enzymes whose sequence is not known.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which enzyme below is fastest?
A) kinase, kcat = 103
B) papain, kcat = 10
C) carboxypeptidase, kcat = 102
D) catalase, kcat = 107
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site of the enzyme. Which statement below correlates with this observation?
A) It must be a competitive inhibitor.
B) The inhibition must be irreversible.
C) It could be noncompetitive or uncompetitive inhibition.
D) It could be irreversible, competitive, noncompetitive or uncompetitive. The data do not relate to the type of inhibition.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is false about covalent modification?
A) It is reversible.
B) It is slightly slower than allosteric regulation.
C) It usually uses the same enzyme for activation and inactivation.
D) All of the above
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The most common enzyme inhibitors are competitive inhibitors.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is difficult to determine either Km or Vmax from a graph of velocity vs. substrate concentration because
A) too much substrate is required to determine them.
B) the graph is sigmoidal.
C) an asymptotic value must be determined from the graph.
D) the points on the graph are often not spread out on the hyperbola.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the known enzymes are .
A) oxidoreductases
B) transferases
C) hydrolases
D) lyases
E) isomerases
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphorylation that changes an enzymeʹs activity is an example of .
A) covalent modification
B) allosteric regulation
C) sequential modification
D) site-directed mutagenesis
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two different substrates react to form two different products, the rate constants for each separate substrate can be determined by
A) varying one substrate at a time, keeping the other in excess.
B) varying both substrates and measuring the appearance of the two products.
C) limiting one substrate and varying the other.
D) keeping both substrate concentrations high and detecting one product at a time.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Select the correct class of enzyme for each of these reactions. A) isomerase B) ligase C) lyase D) transferase E) oxidoreductase F) hydrolase -L-aspartic acid + a-ketoglutarate → oxaloacetic acid + L-Glutamate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of inhibition is indicated by the data graphed below? 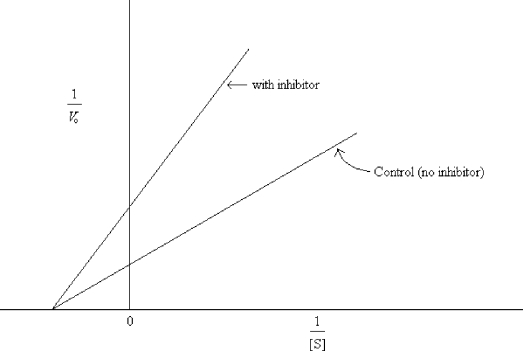
A) competitive
B) uncompetitive
C) noncompetitive
D) irreversible
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
At sufficiently high substrate concentration all types of reversible inhibition can be overwhelmed. At high substrate concentration the enzyme will be saturated and the reaction will proceed at the same maximum velocity as in the absence of inhibitor.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 80
Related Exams