A) is regulated by the government
B) operates in a competitive market
C) has perfect information about consumer demand
D) faces a downward-sloping demand curve
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Khan is a wholesale imported fish distributor. He sells his imported fish to all the restaurants in town and he is the only distributor of a specialty imported fish. Assuming that Khan is maximising his profit, which of the following statements is true?
A) imported fish prices will equal marginal cost
B) imported fish prices will exceed marginal cost
C) imported fish prices will be less than marginal cost
D) imported fish prices will equal average cost
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Adult and concession prices for movie tickets are examples of perfect price discrimination.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist, marginal revenue will turn negative when:
A) the price effect on revenue is greater than the output effect
B) the output effect on revenue is greater than the price effect
C) demand for the good has turned negative
D) An increase in the price results in a fall in demand
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopoly firm has an upward-sloping supply curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-1
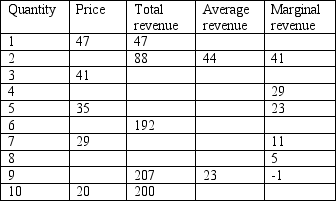 -Refer to Table 15-1. If the monopolist wants to maximise its revenue, how many units of its product should it sell?
-Refer to Table 15-1. If the monopolist wants to maximise its revenue, how many units of its product should it sell?
A) one
B) six
C) eight
D) ten
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 15-2
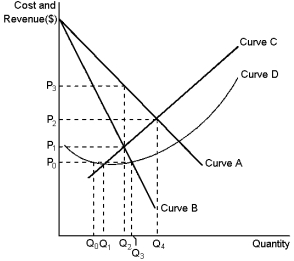 This graph reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-2. Profit will be maximised by charging a price equal to:
This graph reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-2. Profit will be maximised by charging a price equal to:
A) P0
B) P1
C) P2
D) P3
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Competitive firms maximise profit by setting MR = MC. This is not always true for monopoly firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist is a price:
A) setter, and therefore has no indifference curve
B) setter, and therefore has no variable-cost curve
C) setter, and therefore has no supply curve
D) setter, and therefore has no demand curve
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The socially efficient level of production occurs where the marginal-cost curve of a monopoly intersects which of the following curves?
A) demand
B) marginal revenue
C) supply
D) average cost
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a firm operates under conditions of a monopoly, its price is unconstrained.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly will be maximising total welfare if:
A) price equals marginal revenue
B) price equals marginal profit
C) price equals marginal cost
D) the marginal cost curve intersects the marginal revenue curve
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 15-5
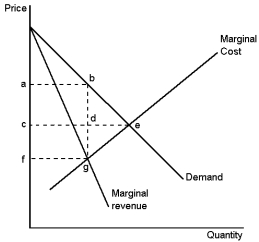 This graph depicts the demand, marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves of a profit-maximising monopolist. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-5. Which of the following areas represents the deadweight loss due to monopoly pricing?
This graph depicts the demand, marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves of a profit-maximising monopolist. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-5. Which of the following areas represents the deadweight loss due to monopoly pricing?
A) rectangle ACDB
B) rectangle CFGD
C) triangle BDE
D) triangle BGE
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 15-1
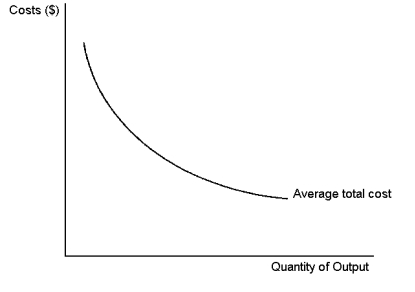 -Refer to Graph 15-1. The shape of the average-total-cost curve in the figure suggests an opportunity for a profit-maximising monopolist to exploit:
-Refer to Graph 15-1. The shape of the average-total-cost curve in the figure suggests an opportunity for a profit-maximising monopolist to exploit:
A) price discrimination
B) average cost pricing
C) economies of scale
D) diminishing marginal product
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government creates a monopoly, the social loss may include:
A) high monopoly profits
B) falling marginal cost
C) the cost of lawyers and lobbyists to convince lawmakers to continue its monopoly
D) all of the above
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 15-2
 This graph reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-2. The marginal-revenue curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve:
This graph reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-2. The marginal-revenue curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve:
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most important feature of a natural monopoly is:
A) constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output
B) it exploits a natural resource
C) diseconomies of scale over the relevant range of output
D) economies of scale over the relevant range of output
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 15-6
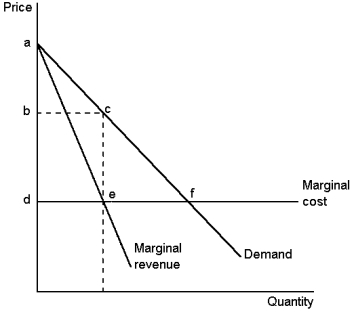 This graph depicts the demand, marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves of a profit-maximising monopolist. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-6. What is the deadweight loss equal to when the monopolist does NOT price discriminate?
This graph depicts the demand, marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves of a profit-maximising monopolist. Use the graph to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Graph 15-6. What is the deadweight loss equal to when the monopolist does NOT price discriminate?
A) ABC
B) ADF
C) CEF
D) deadweight loss will equal zero
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A government created monopoly arises when:
A) government spending in a certain industry gives rise to monopoly power
B) the government gives a firm the exclusive right to sell some good or service
C) the government exercises its market control by encouraging competition among sellers
D) all of the above could qualify as government created monopolies
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal revenue for a monopolist is computed as:
A) total revenue / quantity sold
B) total costs / quantity sold
C) (average revenue * quantity) / price
D) the change to total revenue per unit change in quantity sold
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 159
Related Exams