A) The WLAN is configured at a lower level in the Managed Network hierarchy.
B) The configuration is not deployed to the Mobility Controller (MC) .
C) The Mobility Master (MM) does not have an active PEFNG license.
D) The WLAN is configured as a hidden SSID.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a high-gain omni-directional antenna compare to a typical omni-directional antenna?
A) it provides more coverage in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
B) it provides more single-user spatial streams.
C) it provides more coverage in the horizontal direction than in the vertical direction.
D) it provides more multi-user spatial streams.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the exhibit. 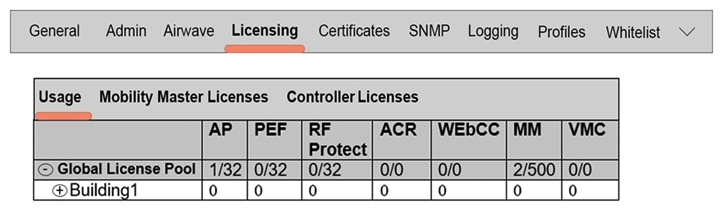 Based on the exhibit, what is the maximum number of APs that this Mobility Master (MM) solution can support?
Based on the exhibit, what is the maximum number of APs that this Mobility Master (MM) solution can support?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 32
D) 500
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An administrator supports a group of employees that connect to the corporate office using the VIA client. An Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) , behind a corporate firewall, terminates the user's VPN sessions. The VPN sessions fail to establish because of the existing firewall rules. Which connections must the administrator allow on the firewall? (Choose three.)
A) TCP 443
B) UDP 8211
C) UDP 8202
D) UDP 500
E) UDP 4500
F) TCP 4443
H) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A network manager wants to implement an Aruba wireless solution that accommodates 802.1X with EAP-TLS. All wireless users will utilize Active Directory (AD) accounts to authenticate. Which device will the authenticator forward the authentication requests to in this type of solution?
A) Mobility Master (MM)
B) Mobility Controller (MC)
C) RADIUS server
D) APs
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference between how a network administrator can monitor clients in the Mobility (MM) interface and in the AirWave Management Platform?
A) AirWave shows trends for the past several minutes, while MM shows longer trends.
B) AirWave combines information from more sources, such as RADIUS authenticating servers and APs.
C) AirWave shows the current signal level for the client connection, while MM does not show RF statistics.
D) MM shows user and role information associated with clients, while AirWave does not.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can network administrator provide high availability for APs deployed in an Aruba Mobility Master (MM) -based architecture?
A) Deploy all licenses locally to APs, so that they can continue to function if they lose contact with their controller.
B) Configure APs to convert to controller-less Instant AP mode during controller failure.
C) Establish clusters of Mobility Controllers (MCs) .
D) Configure MM to provide backup AP tunnel termination in case of controller failure.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An administrator implements two redundant Aruba Mobility Masters (MMs) . Which protocol should the administrator use to detect a failure in a single subnet?
A) PAPI
B) VRRP
C) SNMP
D) IPSec
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A network administrator creates the role employees and adds this rule to it: user any any permit The first several wireless clients assigned to the employees role are assigned IP addresses in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet. Several other wireless clients with the employees role are then assigned IP addresses in the 10.10.20.0/24. When the Aruba firewall matches traffic from these clients to the user any any permit rule, what does it do?
A) It permits traffic from wireless clients in both the 10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.20.0/24 subnet as long as the packet has a source IP.
B) It permits the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.20.0/24 subnet, but drops the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet.
C) It drops traffic from wireless clients in both the 10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.20.0/24 subnet.
D) It permits the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet, but drops the traffic from wireless clients in the 10.10.20.0/24 subnet.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company has an Aruba solution. The company wants to support a guest WLAN with the internal captive portal, but the company also wants to develop their own custom portal pages. What correctly describes the level of customization that the internal captive portal supports?
A) The internal captive portal must use the default pages without modification, but administrators can upload pages developed externally.
B) The internal captive portal must use the default pages without modification, and administrators cannot upload pages developed externally.
C) Administrators can modify the default internal captive portal pages, but cannot upload pages developed externally.
D) Administrators can modify the default internal captive portal pages or upload pages developed externally.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An administrator wants to implement the MultiZone feature in a company's network to segregate corporate and guest traffic. Corporate traffic will have APs establish connections to a cluster managed by a Mobility Master (MM) , and guest traffic will have the same APs establish connections to a standalone controller at the company's DMZ. Given this scenario, what is true about the implementation of MultiZone?
A) Only the primary zone can reboot, upgrade, or provision MultiZone APs.
B) A management session is established only with the primary zone, but data sessions are established to all zones.
C) The primary and data zones must be in the same L2 subnet.
D) A MultiZone AP can initially connect to any zone to obtain its configuration.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company has an Aruba solution with a guest WLAN named exam_guest. A network administrator creates the guest WLAN with the wizard and does not change any of the default roles. The authentication server does not send particular role assignments for authorized users. The company wants to deny guests access to specific IP ranges after the guest authenticate. For which role should the administrator create the rule to deny this traffic?
A) guest
B) authorized
C) exam_guest-guest-logon
D) guest-logon
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A network administrator monitors an Aruba Mobility Controller with Aruba AirWave and sees the configuration status is Error . What should the administrator conclude?
A) AirWave has a communication issue with the controller and cannot check the configuration.
B) AirWave detects a mismatch with the controller configuration and software version.
C) AirWave determines that the controller configuration does not match the template for its group.
D) AirWave checks the controller configuration and detects a syntax error.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which settings can a Mobility Master (MM) deploy to Mobility Controllers (MCs) but master controllers CANNOT deploy to local controllers?
A) radio profiles
B) WLAN settings
C) Interface settings
D) AAA profiles
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An administrator implements a standalone controller that runs ArubaOS 8.x. Which feature should the administrator configure to optimize the RF operation for the company's WLAN?
A) Clustering
B) Zones
C) AirMatch
D) ARM
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company has many 7220 controllers in its Aruba wireless architecture. A network administrator wants to use the Traffic Analysis dashboard in order to monitor which type of applications are being used by wireless users. What is required for this implementation?
A) AirMatch and ClientMatch must be enabled.
B) The solution must have active PEFNG licenses.
C) WLANs must use the decrypt-tunnel forwarding option.
D) Firewall policies must include application filtering rules.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A customer has a large campus that requires 400 Aruba 335 APs to support a total of 10,000 wireless users and 12Gbps of traffic. Although the customer wants two controllers for redundancy, each controller must be able to support all of the APs and users on its own. Which Aruba Mobility Controller models meet the customer requirements and DO NOT unnecessarily exceed them?
A) Aruba 7030 controllers
B) Aruba 7024 controllers
C) Aruba 7240 controllers
D) Aruba 7210 controllers
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An Aruba solution runs ArubaOS 8 and uses a mobility master architecture. Which feature can network administrators use to balance wireless across APs on different channels?
A) AppRF
B) ARM
C) Client Match
D) AirMatch
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which task can an Aruba Spectrum Monitor (SM) perform?
A) Prevent client connections to rogue APs.
B) Analyze RF signals to determine the cause of non-802.11 interference.
C) Optimize RF through the AP channel and transmit power plans.
D) Analyze wireless traffic patterns at the application level.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does WPA2 protect wireless user traffic in the air?
A) It provides both data integrity and privacy with AES.
B) It provides data integrity with TKIP and data privacy with AES.
C) It provides data privacy with TKIP and no data integrity.
D) It provides data integrity with AES and no data privacy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 23
Related Exams