Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can result in chain termination in cationic polymerization?
A) loss of H+
B) addition of a nucleophile that reacts with the propagating site
C) a chain transfer reaction with the solvent
D) a 1,2-hydride shift.
E) A,B,and C
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best explains the process known as chain transfer?
A) a process that can control the rate of production of the polymer
B) a process that can control the molecular weight of the polymer
C) a process that can control the reactivity of the monomer
D) a process that can slow down the polymerization reaction
E) a process that can inhibit the polymerization reaction
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Show the reaction which occurs when benzoyl peroxide is heated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Describe what thermoplastic polymers are.
Correct Answer

verified
Polymers that have both ordered crystall...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
Draw the structure of the polymer and by-product that result when the two monomers below are heated together. 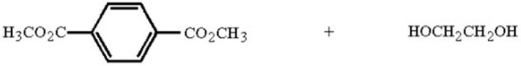
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following monomers is least likely to undergo cationic polymerization?
A) propylene
B) isobutylene
C) styrene
D) methyl acrylate
E) vinyl acetate
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a step-growth polymer?
A) Nylon 66
B) Kevlar
C) Mylar
D) Lexan
E) Teflon
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw the products which would result if poly(ethylene terephthalate)were hydrolyzed in hot aqueous NaOH.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a step-growth polymer?
A) polyethylene
B) polyester
C) polypropylene
D) polystyrene
E) Plexiglass
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the first chain propagating step in the radical polymerization of ethylene?
A) ROOR + CH2 ![]() CH2 → ROCH2CH2OR
CH2 → ROCH2CH2OR
B) ∙ RO∙ + CH2
![]() CH2 → ROCH2CH2
CH2 → ROCH2CH2
C) RO∙ + CH2 ![]() CH2 → ROCH
CH2 → ROCH ![]() CH2 + H∙
CH2 + H∙
D) ∙ ∙ ROOR + CH2
![]() CH2 → 2 ROH + CH
CH2 → 2 ROH + CH ![]() CH
CH
E) ∙ ∙ 2RO∙ + CH2
![]() CH2 → 2 ROH + CH
CH2 → 2 ROH + CH ![]() CH
CH
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the structure of poly(vinyl chloride).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Give the monomer for the polymer teflon.
A) propylene
B) acrylonitrile
C) tetrafluoroethylene
D) poly(vinyl acetate)
E) styrene
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following addition polymers results from the reaction below? nCF2
![Which of the following addition polymers results from the reaction below? nCF<sub>2</sub> <sub> </sub> CF<sub>2 </sub> <sub> </sub> ? A) [ CF-CF ]<sub>n</sub> B) [CF<sub>3</sub>-CF<sub>3</sub>]<sub>n</sub> C) [-CF<sub>2</sub>-CH CHCF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub> D) [-CF<sub>2</sub>-CF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub> E) [-CF<sub>2</sub> <sub> </sub> CF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1831/11ea8a1c_2db3_6426_b657_6bcecbfae464_TB1831_11.jpg) CF2
CF2
![Which of the following addition polymers results from the reaction below? nCF<sub>2</sub> <sub> </sub> CF<sub>2 </sub> <sub> </sub> ? A) [ CF-CF ]<sub>n</sub> B) [CF<sub>3</sub>-CF<sub>3</sub>]<sub>n</sub> C) [-CF<sub>2</sub>-CH CHCF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub> D) [-CF<sub>2</sub>-CF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub> E) [-CF<sub>2</sub> <sub> </sub> CF<sub>2</sub>-]<sub>n</sub>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1831/11ea8a1c_2db3_6427_b657_c10f968857e3_TB1831_11.jpg) ?
?
A) [ ![]() CF-CF
CF-CF ![]() ]n
]n
B) [CF3-CF3]n
C) [-CF2-CH ![]() CHCF2-]n
CHCF2-]n
D) [-CF2-CF2-]n
E) [-CF2 ![]() CF2-]n
CF2-]n
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What are biodegradable polymers? Give an example.
Correct Answer

verified
Polymers that can be broken into smaller...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Give the product for an diisocyanate reacting with a diol.
A) an epoxy resin
B) a polyester
C) a polycarbonate
D) a polyamide
E) a polyurethane
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw a segment of the polymer,using four monomers. 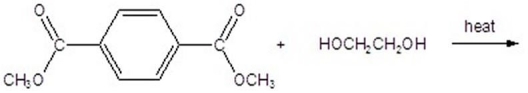
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the structure of the monomer from which the following polymer is made? 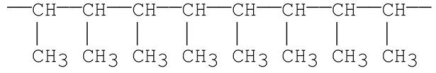
A) CH3CH3
B) CH2 ![]() CH2
CH2
C) CH3CH ![]() CH2
CH2
D) CH2 ![]() CHCH
CHCH ![]() CH2
CH2
E) CH3CH ![]() CHCH3
CHCH3
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kevlar is one of the hardest polymer known.The exceptional strength of Kevlar is attributed to
A) amide bonds between the chains that form a sheet-like structure.
B) ester bonds between the chains that form a sheet-like structure.
C) disulfide bonds between the chains that form a sheet-like structure.
D) hydrogen bonds between the chains that form a sheet-like structure.
E) none of the above
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The joining together of many monomers to form a very large molecule is called
A) polymerization.
B) monomerization.
C) dimerization.
D) hydroxylation.
E) homogenization.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 116
Related Exams