Correct Answer

verified
Individuals with Cori disease ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
The hormone insulin stimulates __________ and inhibits __________,leading to a(n) __________ in the glucose levels.
A) glycogen synthase; glycogen phosphorylase; decrease
B) glycogen phosphorylase; glycogen synthase; decrease
C) glycogen synthase; glycogen phosphorylase; increase
D) glycogen phosphorylase; glycogen synthase; increase
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
List the three enzymes in glycolysis that are bypassed in gluconeogenesis and match them with the enzymes in gluconeogenesis that replace them.
Correct Answer

verified
(1)Hexokinase is replaced by glucose-1-p...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
What triggers the Cori cycle?
A) a buildup of cellular NAD+
B) oxygen-limited working muscle cells
C) low levels of glucose in the muscle cells
D) elevated glucagon levels
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which enzyme class catalyzes the following pentose phosphate pathway reaction (note that there may be some missing reactants and products) ? 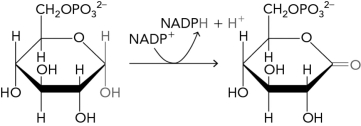
A) lyase
B) isomerase
C) transferase
D) oxidoreductase
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw a glucose molecule and indicate which atom is linked to glycogen during the glycogen synthesis process.
Correct Answer

verified
The C1 of the incomi...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
The opposing glycolysis and gluconeogenesis enzymes hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase are located with which cellular locations,respectively?
Correct Answer

verified
Hexokinase is found in the cyt...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules would activate phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1) ?
A) NADH
B) AMP
C) ATP
D) pyruvate
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the ratio of NADP+ to NADPH were high,the
A) net production of ATP would occur.
B) pentose phosphate pathway oxidative phase would be activated.
C) cellular levels of nucleotides would have to increase from an activated pentose phosphate pathway.
D) pentose phosphate pathway would be inhibited.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the enzyme that removes phosphate groups from the regulated glycogen metabolism enzymes to reverse their activity?
A) phosphorylase kinase
B) protein phosphatase 1
C) insulin
D) protein kinase A
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many of the 10 glycolysis reactions use the same enzyme in the gluconeogenesis pathway?
A) 10
B) 7
C) 5
D) 3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The branching enzyme
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What are the three main sources of carbon in animals making glucose with the gluconeogenesis pathway?
Correct Answer

verified
(1)Glycerol from fats,(2)lacta...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which correctly describes the role of the transport system shown below? 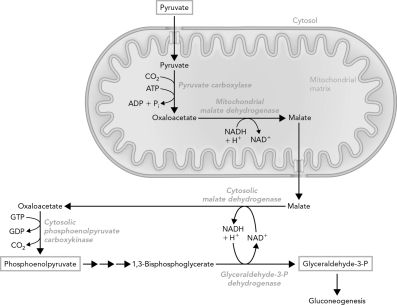
A) It provides an alternate fate for pyruvate degradation.
B) It provides a source of NADH for gluconeogenesis via malate transport.
C) It converts NADH equivalents into reduced forms of carbon.
D) It allows for pyruvate transport into and out of the mitochondria.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What molecule activates the pentose phosphate pathway?
A) NADP+
B) ribulose-5-phosphate
C) ADP
D) NADH
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main function of the pentose phosphate pathway is to provide
A) the cell with backup capability when glycolysis is inhibited.
B) energy and reducing power.
C) a mechanism for the utilization of the carbon skeletons of excess amino acids.
D) a source of ribose and NADPH.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pentose phosphate pathway
A) resembles the TCA cycle in that it couples the loss of CO2 with the formation of NADH.
B) allows 5C sugars to converge with or diverge from the glycolysis pathway.
C) contains 2C, 3C, 4C, 5C, 6C, and 7C sugar molecules.
D) enables the production of ATP from glucose.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
What class of enzymes in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway is responsible for the production of NADPH?
Correct Answer

verified
Dehydrogen...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules might inhibit the regulated enzymes in glycolysis?
A) NAD+
B) ATP
C) AMP
D) fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is involved in the breakdown of glycogen?
A) inorganic phosphate
B) ATP
C) branching enzyme
D) hexokinase
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 100
Related Exams