Use the following to answer questions:
The diagram below shows how DNA is sequenced. 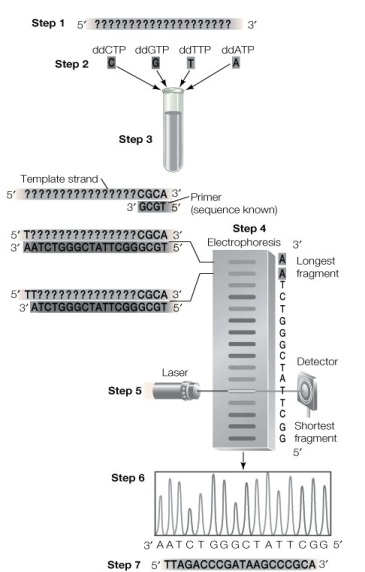 -At which step are the DNA segments first separated by length?
-At which step are the DNA segments first separated by length?
A) Step 2
B) Step 3
C) Step 4
D) Step 5
E) Step 6 or later
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Which of the following fields or approaches is most likely to lead directly to a reduction in the negative side effects associated with a drug used to treat diabetes?
A) Comparative genomics
B) Metagenomics
C) Metabolomics
D) Pharmacogenomics
E) Selective inactivation
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified