A) 0.158 nm
B) 0.316 nm
C) 0.474 nm
D) 0.632 nm
E) 1.26 nm
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a single-slit diffraction pattern, the central maximum is about twice as wide as the other maxima. This is because:
A) half the light is diffracted up and half is diffracted down
B) the central maximum has both electric and magnetic fields present
C) the small angle approximation applies only near the central maximum
D) the screen is flat instead of spherical
E) none of the above
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Radio waves are readily diffracted around buildings whereas light waves are negligibly diffracted around buildings. This is because radio waves:
A) are plane polarized
B) have much longer wavelengths than light waves
C) have much shorter wavelengths than light waves
D) are nearly monochromatic (single frequency)
E) are amplitude modulated (AM)
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
600-nm light is incident on a defraction grating with a ruling separation of 1.7*10-6 m. The second order line occurs at a diffraction angle of:
A) 0
B) 10
C) 21
D) 42
E) 45
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a diffraction line phasors associated with waves from the slits of a multiple-slit barrier:
A) are aligned
B) form a closed polygon
C) form a polygon with several sides missing
D) are parallel but adjacent phasors point in opposite directions
E) form the arc of a circle
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sound differs from light in that sound:
A) is not subject to diffraction
B) is a torsional wave rather than a longitudinal wave
C) does not require energy for its origin
D) is a longitudinal wave rather than a transverse wave
E) is always monochromatic
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A diffraction-limited laser of length 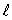 and aperture diameter d generates light of wavelength . If the beam is directed at the surface of the Moon a distance D away, the radius of the illuminated area on the moon is approximately:
and aperture diameter d generates light of wavelength . If the beam is directed at the surface of the Moon a distance D away, the radius of the illuminated area on the moon is approximately:
A) ![]()
B) dD/
C) ![]()
D) D /d
E) ![]()
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student wishes to produce a single-slit diffraction pattern in a ripple tank experiment. He considers the following parameters:  Which two of the above should be decreased to produce more bending?
Which two of the above should be decreased to produce more bending?
A) I, III
B) I, IV
C) II, III
D) II, IV
E) III, IV
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bragg's law for x-ray diffraction is 2d sin = m , where is the angle between the incident beam and:
A) a reflecting plane of atoms
B) the normal to a reflecting plane of atoms
C) the scattered beam
D) the normal to the scattered beam
E) the refracted beam
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A beam of x-rays of wavelength 0.20 nm is diffracted by a set of planes in a crystal whose separation is 3.1* 10-8 cm. The smallest angle between the beam and the crystal planes for which a reflection occurs is:
A) 0.70 rad
B) 0.33 rad
C) 0.033 rad
D) 0.066 rad
E) no such angle exists
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two nearly equal wavelengths of light are incident on an N slit grating. The two wavelengths are not resolvable. When N is increased they become resolvable. This is because:
A) more light gets through the grating
B) the lines get more intense
C) the entire pattern spreads out
D) there are more orders present
E) the lines become more narrow
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
X rays are:
A) electromagnetic waves
B) negatively charged ions
C) rapidly moving electrons
D) rapidly moving protons
E) rapidly moving neutrons
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A diffraction grating just resolves the wavelengths 400.0 nm and 400.1 nm in first order. The number of slits in the grating is:
A) 400
B) 1000
C) 2500
D) 4000
E) not enough information is given
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As more slits with the same spacing are added to a multiple-slit system the lines:
A) spread further apart
B) move closer together
C) become wider
D) becomes narrower
E) do not change in position or width
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure (i) shows a double-slit pattern obtained using monochromatic light. Consider the following five possible changes in conditions:  Which of the above would change Figure (i) into Figure (ii) ?
Which of the above would change Figure (i) into Figure (ii) ? 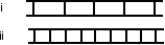
A) 3 only
B) 5 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1 and 5 only
E) 2 and 4 only
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the equation sin = /a for single-slit diffraction, is:
A) the angle to the first minimum
B) the angle to the second maximum
C) the phase angle between the extreme rays
D) N where N is an integer
E) (N + 1/2) where N is an integer
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the minimum number of slits required in a deffraction grating to just resolve light with wavelengths of 471.0 nm and 471.6 nm?
A) 99
B) 197
C) 393
D) 786
E) 1179
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to obtain a good single-slit diffraction pattern, the slit width could be:
A)
B) /10
C) 10
D) 104
E) /104
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A diffraction grating of width W produces a deviation in second order for light of wavelength . The total number N of slits in the grating is given by:
A) 2W /sin
B) (W/ ) sin
C) W/2sin
D) (W/2 ) sin
E) 2 /sin
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the equation d sin = m for the lines of a diffratction grating m is:
A) the number of slits
B) the slit width
C) the slit separation
D) the order of the line
E) the index of refraction
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 74
Related Exams